Visual Weld Inspection Acceptance Criteria
So if we have chosen for Normal Pipe Service to have at least 5% of welds X-Rayed does that then replace the requirements of Visual Inspection (P 344.2) as only one method of inspection is required. All welders visually inspect their own work of course, but for Code acceptance is 5% X-ray all that is required, or am i misinterpreting P 344.1.1. WO #541005 -Attachment 2 -Visual Weld Inspection Reports VISUAL WELD INSPECTION REPORT (See Note) Work Package No.: 541005 IFaclllty: 2025E Company: QCHPRC QMSA @WRPS Drawing No. (if applicable): ECN-715052 Rev.: 1 11napec11on Proc.: HNF-54260 Rev.: 2 Acceptance Criteria: 1001 Visual & 51 RT per ASHE B31.3, Normal Fluid Service Weld or Step Welding Welder ID(s)I. What is the correct Visual Inspection Acceptance Criteria time for inspection for ASTM A 709 Grade 100 and 100W? Visual Inspection performed not less than 48 hours after completion b. Inspections of welds can begin immediately after welds has been completed. Inspections of welds can begin after welds have cooled to ambient temperature.
During the fabrication process of equipment, we often encounter the welding process. Welding inspector officers have the duty to maintain welding quality. This QA / QC process starts from weld preparation, weld process and after welding. The welding inspector has several kinds of certifications. For Europe, we are familiar with welding inspectors CSWIP 3.0 and CSWIP 3.1. In November 2019, I took part in the training and examination of the CSWIP 3.0 Welding Inspector certification in addition to my previous competence, which was a certified welding engineer. The CSWIP 3.0 Visual Welding Inspector course is designed for welders, operators, line inspectors, and foremen who carry out the visual examination of welded joints. It is also suitable for welding quality control staff and anyone who needs basic training in welding inspection alongside a qualification. Construction engineers also need to understand welding inspection.
CSWIP 3.0 training (course and exam) duration
The training lasts for 3 days. 2 days are used to study the types of welding defects, limits and acceptance criteria, and practice questions. then 1 day is used for the test. The exam only lasts for 2 hours. The participants worked on 20 questions about welding on plates (butt weld) and 14 questions on welding plates with fillet weld types. Free avg tuneup pro. The minimum score is 70% for butt weld and 70% for fillet weld. After attending this training, the participant should be able to :
- Identify various weld imperfections (defects) that can be inspected visually
- Understand the relevant welding technology related to visual inspection for plate
- Understand the requirement for documentation/report in welding inspection
- Understand codes and standards in Europe related to inspection requirements of butt weld and fillet weld in a plate
- Carry out inspection of base materials and consumables materials (electrodes, filler wires, consumable inserts, gases, fluxes etc)
- Carry out visual inspection of welds, report on them and assess their compliance with specified acceptance criteria
- Verify weld dimensions, fit up and weld preparations are in accordance with the engineering drawings.
- Pass the CSWIP Visual Welding Inspector qualification.
How to join CSWIP 3.0 Training and examination? You can join the training in your country by contacting TWI agent. Usually, the minimum participant is 10.
what is CSWIP?
CSWIP stand for Certification Scheme for Personnel. Why we choose CSWIP? CSWIP is a complete or comprehensive scheme which provides for the examination and certification of professional / individuals seeking to demonstrate their knowledge and/or competence in their field of operation. The scope of CSWIP includes among others, Welding Inspectors, Welding Supervisors, Welding Instructors, Welding Examiners, Welding Quality Control Coordinators, Heat Treatment Operatives, Cathodic Inspection personnel, Plant Inspectors, Underwater Inspectors, Plastics Welders and NDT personnel. CSWIP focus mainly on welding and inspection knowledge & certification.
CSWIP is managed by the Certification Management Board, which acts as the Governing Board for Certification, in keeping with the requirements of the industries served by the scheme. The Certification Management Board, in turn, appoints specialist Management Committees to oversee specific parts of the scheme. All CSWIP Boards and Committees comprise member representatives of relevant industrial and other interests. TWI Certification Ltd is accredited by UKAS to BS EN ISO/IEC 17024 for certification of personnel.
D1.1 Visual Acceptance Criteria
Responsibility of CSWIP 3.0 welding Inspector
after we joined CSWIP 3.0 visual welding inspection course and pass the exam, we have responsibility in the area of visual welding inspection.
- Post weld visual inspection
Visual inspection and dimensional check of completed weld against specification requirements and drawings.
and under the supervision of a Welding Inspector or Senior Welding Inspector: - Establish the most suitable welding processes
- Codes and standards
Application of the requirements of codes and standards. - Parent material identity
Verification against documentation and markings of correctness of parent material. - Welding consumables identity
Verification of correctness of welding consumables (electrodes, filler wires, consumable inserts, gases, fluxes etc). - Pre-weld inspection
Verification that dimensions, fit up and weld preparations are in accordance with the engineering drawings. - Preheating
Verification that preheat (where required) is in accordance with specified procedures. - In-process welding surveillance
Surveillance during welding to verify compliance with specified procedure including any preheat, interpass temperature control and post heat requirements.
CSWIP 3.0 Course Objectives:
- To identify various weld imperfections (defects)
- To understand the relevant welding technology related to visual inspection
- To understand the need for documentation in welding
- To be aware of codes and standards related to inspection requirements
- To carry out inspection of parent materials and consumables
- To carry out visual inspection of welds, report on them and assess their compliance with specified acceptance criteria
- To pass the CSWIP 3.0 Visual Welding Inspector qualification.
Additional Information for CSWIP 3.0 training course:
Examination applicants must submit a detailed CV/resume when booking this course.
Enrolment on this course does not constitute reservation of an examination. All courses may be followed by a CSWIP Welding Inspector examination for candidates with appropriate experience as specified in CSWIP document WI-6-92. All CSWIP requirement documents are available at www.cswip.com.
Entry Requirements for participant:
Although there is no specific experience required, it is recommended that candidates possess a minimum of six months’ welding-related engineering experience and two years’ industrial experience. In addition, candidates must comply with Clause 1.3.4 of CSWIP document WI-6-92 available at www.cswip.com.
During training, participant will receive some books related to Visual welding inspection, example of questions for exam, CSWIP acceptance criteria and plates for practical purposes.
Career Progression after completing CSWIP 3.0:
- CSWIP 3.1 – Welding Inspector – Level 2
- CSWIP 3.2 – Senior Welding Inspector – Level 3
Best Practices for CSWIP 3.0 training and exam participants:
- make sure you learned about welding technology, welding defect and visual welding inspection tools before attend the training. At least you familiar with welding defect terminology such as burn out, lack of penetration that can be observed by visual method.
- During training, pay attention on acceptance criteria for each defect.
- Do your exam trial by your self, and rate your self. If you have lack of understanding about some defect criteria, do not hesitate to discuss with the trainer. CSWIP acceptance criteria is not same with ASME acceptance criteria.
- Be calm. Do not panic.
- Do not cheat
- Take a rest and prepare your self before the exam day.
key word for CSWIP 3.0 training and exam:
- understanding welding defect
- able to measure the defect
- able to compare the defect to CSWIP acceptance criteria
Visual Weld Inspection Criteria
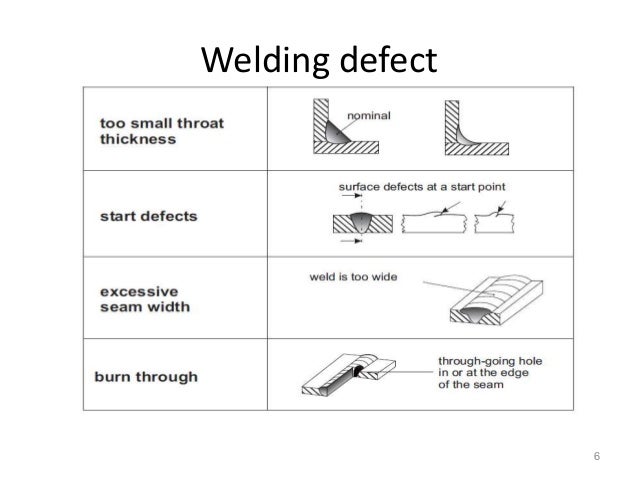
Visual Weld Inspection Acceptance Criteria Sample
Aws Visual Inspection Criteria

Visual Weld Inspection Acceptance Criteria Aws D1.1
Visual Weld Inspection Guide
Visual Weld Inspection Acceptance Criteria Asme B31.3
